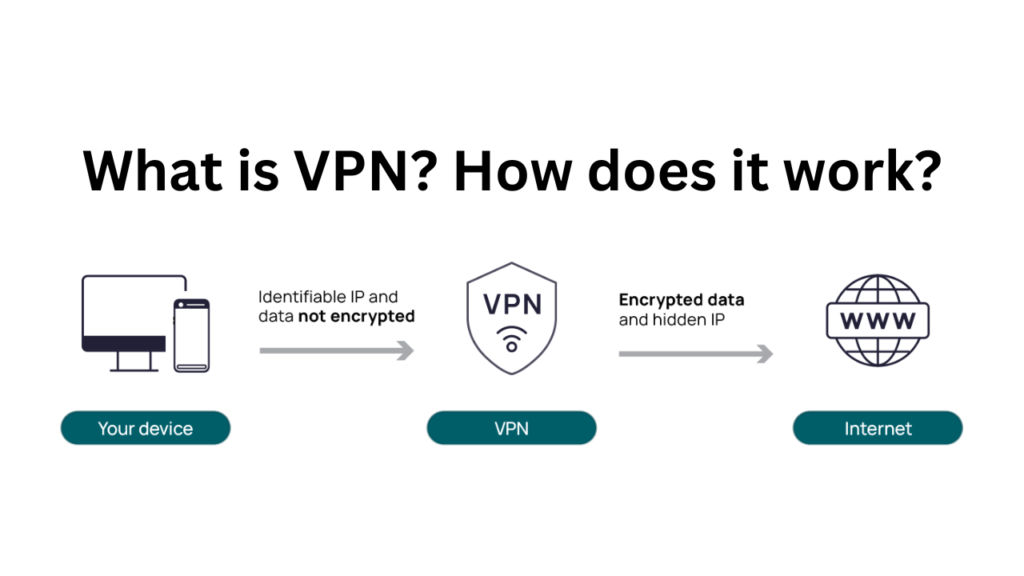
VPN hides the internet data coming and going from the device. This software resides on the device and sends the data by encrypting it.
Due to encryption, the data becomes unreadable to anyone. VPN creates a digital connection between the computer and the VPN provider’s remote server.
Read More: How to Transfer a Domain Name from GoDaddy to Google Domains?
How does a VPN work?
This connection acts like a point-to-point tunnel, which encrypts data and hides the IP address.
With the help of a VPN, blocked websites and firewalls on the Internet can also be bypassed!
This ensures that the data cannot be read unless someone unlocks it with a password, known as an encryption key.
When using a VPN, the encryption keys that protect a user’s data and web activity are known only by their computer and the VPN server.
How to use a VPN
Go to the company’s website whose VPN you want to use and register. For that, you will need Email and Password.
After providing these details, you will be able to register. If you receive a verification link or code on your email, confirm it.
Then you can use VPN by downloading the Chrome Extension of the software from the VPN website.
Who should use a VPN?
If you are using the internet for normal work, then you can use any browser without a VPN. But if you do not want your IP address to be tracked or you want to use such websites or applications that are banned in your country, then you can take the help of a VPN to use them.
Types of VPN
There are many types of VPNs, but you should be familiar with the three main types:
SSL VPN :
Often not all employees of a company have access to company laptops that they can use to work from home. During the coronavirus crisis in spring 2020, many companies faced the problem of not having enough equipment for their employees.
In such cases, personal devices (PC, laptop, tablet, mobile phone) are often used. In this case, companies fall back on the SSL-VPN solution, which is usually implemented via a corresponding hardware box.
Typically an HTML-5-enabled browser is required, which is used to call up the company’s login page. HTML-5-enabled browsers are available for virtually any operating system. Access is protected with a username and password.
Site-to-site VPN :
A site-to-site VPN is essentially a private network designed to hide private intranets and allow users of these secure networks to access each other’s resources.
A site-to-site VPN is useful if your company has multiple locations, each with its local area network (LAN) connected to a WAN (wide area network). Site-to-site VPNs are also useful if you have two separate intranets between which you want to send files without users of one intranet having explicit access to the other intranet.
Site-to-site VPNs are used mainly in large companies. They are complex to implement and do not offer the same flexibility as SSL VPNs. However, they are the most effective way to ensure communications within and between large departments.
Client-to-Server VPN :
Connecting via a VPN client can be imagined as if you were connecting your home PC to the company one with an extension cable. Employees can dial into the company network from their home office via a secure connection and act as if they were sitting in the office. However, a VPN client must first be installed and configured on the computer.
This involves the user not connecting to the internet through their own ISP, but rather establishing a direct connection through their VPN provider. This essentially shortens the tunnel phase of the VPN journey. Instead of using a VPN to create an encryption tunnel to hide an existing internet connection, the VPN can automatically encrypt the data before making it available to the user.
This is an increasingly common form of VPN, which is particularly useful for insecure public WLAN providers. It prevents third parties from accessing and compromising the network connection and encrypts the data up to the provider.
It also prevents the ISP from accessing data that, for whatever reason, remains unencrypted and bypasses any restrictions on the user’s Internet access (for example, if the government of that country restricts Internet access).
The advantage of this type of VPN access is greater efficiency and universal access to company resources. Provided a suitable telephone system is available, for example, the employee can connect to the system with a headset and act as if he were at his company’s workplace.
For example, the company’s customers cannot even tell whether the employee is at work at the company or his home office.